Wireless Sensors
//code.Node
//code.NodeThe //code.Node has six interactive sensors and four device outputs that measure and respond to phenomena using code created in SPARKvue or Capstone software.
//code.Node Holder
//code.Node HolderThis convenient holder for the //code.Node has Velcro to attach to a wall or strap around your arm.
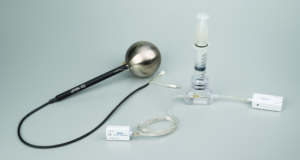
Ammonium Ion Selective Electrode
Ammonium Ion Selective ElectrodeThis ISE connects to the Wireless pH Sensor and allows students to measure ammonium concentration in an aqueous solution.
Ballistic Pendulum – Wireless
Ballistic Pendulum – WirelessUse conservation of energy and conservation of momentum to determine the muzzle velocity of a projectile.
Calcium Ion Selective Electrode
Calcium Ion Selective ElectrodeThis ISE connects to the Wireless pH Sensor and allows students to measure the concentration of Calcium ions in aqueous solutions.
Carbon Dioxide Ion Selective Electrode
Carbon Dioxide Ion Selective ElectrodeThis ISE connects to the Wireless pH Sensor and allows students to measure carbon dioxide concentration in an aqueous solution.
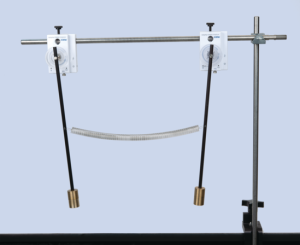
Centripetal Force on a Pendulum – Wireless
Centripetal Force on a Pendulum – WirelessMotion of pendulum experiment shows mass, radius, angular velocity and centripetal force relationship using wireless sensors.
Chloride Ion Selective Electrode
Chloride Ion Selective ElectrodeThis ISE connects to the Wireless pH Sensor and allows students to measure the concentration of chloride ion in an aqueous solution.
Conservation of Energy II – Wireless
Conservation of Energy II – WirelessThe complete solution for observing the conservation of energy as it is converted from potential to kinetic energy.
Dissolved CO₂ Waterproof Sleeve
Dissolved CO₂ Waterproof SleeveThe Wireless CO₂ Sensor can be equipped for aqueous measurements using this semipermeable sleeve.
Includes; 5 x sleeves & 5 x O-rings
Electrical Equivalent of Heat – Wireless
Electrical Equivalent of Heat – WirelessA Wireless Current Sensor and a Wireless Voltage Sensor are used to measure the electrical power delivered to the resistor that is heating the water and a Wireless Temperature Sensor is used to measure the increase in temperature of the water.
Faraday’s Law of Induction – Wireless
Faraday’s Law of Induction – WirelessA voltage is induced in a coil swinging through a magnetic field. Faraday’s Law and Lenz’s Law are examined and the energy dissipated in a load resistor is compared to the loss of energy of the coil pendulum.
Flat pH Probe
Flat pH ProbeAllows students to measure pH in low moisture, non-aqueous items. Intended for use with the Wireless pH Sensor.
Heat Engine Cycle – Wireless
Heat Engine Cycle – WirelessA P-V diagram is generated as a heat engine is taken through a cycle. From this diagram, the heat added to the gas and the work done by the engine are measured to determine the efficiency of the engine. This actual efficiency is compared to the theoretical maximum efficiency.
Ideal Gas Law – Wireless
Ideal Gas Law – WirelessIn this experiment designed for use with PASCO Capstone software, the temperature, volume, and pressure of a gas are measured simultaneously to show that they change according to the Ideal Gas Law.
Interference and Diffraction – Wireless
Interference and Diffraction – WirelessInterference and diffraction patterns from laser light passing through various single-slits and multiple-slits are scanned and plotted in real time. These patterns are then examined for similarities and differences.
Magnetic Fields of Coils – Wireless
Magnetic Fields of Coils – WirelessThe dependence of the magnetic field strength of current-carrying coils on the distance from the coil along the perpendicular axis is determined and compared to the theoretical curve. In addition, the effect of varying the coil separation on the shape of the magnetic field between the Helmholtz coils is examined.
Nitrate Ion Selective Electrode
Nitrate Ion Selective ElectrodeThis ISE connects to the Wireless pH Sensor and allows students to measure the concentration of nitrate ions in aqueous solutions.